Cybercriminals have turned the coronavirus pandemic into a scam pandemic as well—find out how to avoid being victimized.
In its early days, the Business Email Compromise (BEC) attack typically began with hacking or spoofing email accounts of CEOs or CFOs of businesses, and then requesting fund transfers to accounts controlled by the criminals.
Since then, these attacks have grown in sophistication, mostly in the social engineering aspect. Rather than targeting the companies directly, attackers now target customers, HR departments, suppliers, related accountants, and law firms, and even tax authorities. In addition to directly generating or diverting currency transactions, BEC attacks have also been used to make fraudulent purchases, divert tax returns, and even transfer millions of dollars’ worth of hardware and equipment into the control of cybercriminals.
To help with their social engineering attempts, criminals love to tap into major current events or news stories. Since January 2020, they have had the perfect vehicle for scams with the COVID-19 outbreak and subsequent pandemic. The new working conditions enforced by the global outbreak has triggered a spike in BEC scams, because more remote-working means more opportunities to catch users off guard.
Check Point Research recently showed a 30% increase in COVID-19 related cyber-attacks over the first two weeks of May, many of which involved email scams. On average, there were 192,000 coronavirus-related cyber-attacks documented per week.
Multiple incidents have been reported of government agencies and medical services, which, while attempting to procure medical equipment, transferred funds to fraudulent brokers prior to receiving the items, only to learn that the equipment did not exist, and that the funds are unrecoverable.
What is behind a BEC attack?
Let us look at the components of a basic BEC attack. An attacker typically constructs an email that impersonates a high-level executive of a company—either by hacking into the organization’s email system, or by designing a legitimate-looking fake—and sending it to an employee, requesting a transfer of money to a bank account under the attackers’ control. This is often done with the excuse of urgency or communication problems to prevent the manager from having time to communicate in alternative ways.
The three main ways of impersonation are:
- The attacker spoofs the source email address: as the basic SMTP protocol does not provide a sender validation mechanism, attackers can use either dedicated or publicly-exposed SMTP servers to send emails with a spoofed sender address.
- The attacker sends emails from the authentic email account of the impersonated victim by gaining control of their email account through phishing, credentials theft, or other means.
- The attacker sends an email using a look-alike domain which they have already set up. In this case, the domain differs from the authentic address by a minor detail, such as sending an email from “example.co” rather than “example.com”.
BEC scams hit all sectors of commerce, from real-estate to art, government, municipalities and even the military. In one such fraud that was exposed in 2019, a US defence contractor was tricked into sending equipment for a fake order worth over US$10 million, including US$3.2 million in highly-sensitive communications interception equipment.
The attacker had sent a phony purchase order using a fake Yahoo! email address ending in “navy-mil.us”. In addition to the use of a fake email account, the success of such BEC frauds requires detailed knowledge of the identity of the victims to contact, the tone and phrasing of the purchase order and communication jargon, and knowledge of the right equipment to order.
Organized crime fueling BEC
Often, these sophisticated attacks are not conducted by a single individual but by an infrastructure typical to organized crime. Operations demand bank accounts to be established, which often require the use of stolen identities obtained in underground markets or stolen in separate operations. Stolen funds must be withdrawn by multiple individuals and transactions, which involves complex logistics of money mules, often in international operations.
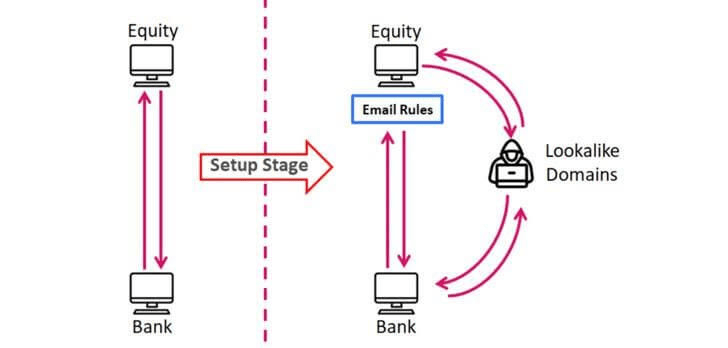
In a sophisticated BEC attack recently exposed by Check Point Research, the attackers infiltrated the o365 email accounts of three financial firms and monitored all correspondence for several weeks. They then created lookalike domains for the attacked firms, as well as the corresponding partners, accountants and banks, and then diverted relevant communication to the fake domains. This created a “man-in-the-middle” scheme (figure) which allowed them to divert and initiate fraudulent money transfers of more than US$1.3 million.
Such attacks are more complicated to terminate even after their exposure since an unknown number of customers and service providers may still be unknowingly conducting correspondence directly with the attackers.
Intervention in such operations requires international law enforcement cooperation in networks spread over several continents. One such operation, revealed in September 2019, resulted in the arrest of 281 suspects located in 10 countries, as well as the recovery of US$120 million in confiscated and recovered wire transfers.
From gift cards to military equipment
Direct money transfers are not the only way to steal money through BEC attacks. In many cases, it is easier to persuade company officials to buy gift cards rather than make a direct fund transfer. In this way, attackers are not required to create fraudulent bank accounts and gift card details can be sold online in forums for about 70% of their actual value.
Attacks with gift cards are especially widespread during holiday seasons, and getting money back is nearly impossible. The most popular gift card suppliers used in BEC frauds are Google Play, eBay, Target, and Walmart and according to researchers, this technology is used in more than 60% of BEC accidents.
So how can you improve your organization’s resilience to BEC attacks? Here are our tips:
- Protect your email traffic with at least one layer of an advanced email security solution from a known vendor.
- Protect mobile and endpoint browsing with advanced cybersecurity solutions that prevent browsing to phishing web sites, whether known or unknown.
- Use two-factor authentication to verify any change to account information or wire instructions.
- Continuously educate your end users: whenever irreversible actions such as money transfers are conducted, details of the transaction must be verified via additional means such as voice communication and must not exclusively rely on information from email correspondence.
- Check the full email address on any message and be alert to hyperlinks that may contain misspellings of the actual domain name.
- Do not supply login credentials or personal information in response to a text or email.
- Follow security best practices.
- Regularly monitor financial accounts.
- Keep all software and systems up to date.
- Use an email security solution that blocks sophisticated phishing attacks like BEC, in order to prevent them from reaching employees mailboxes to begin with.